Difference Between Open Source Software and Freeware Software
اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر اور فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر کے درمیان فرق

Introduction: In the field of Library and Information Science (LIS), understanding different types of software is crucial for managing digital libraries, databases, and information systems. Today, we will discuss two commonly misunderstood software categories: Open Source Software and Freeware Software. These terms are frequently used in the context of software distribution, but they have distinct differences in terms of licensing, usage, and access to the software’s source code.
Objectives:
- Define Open Source Software and Freeware.
- Compare the key differences between the two.
- Understand the implications of each for Library and Information Science (LIS) professionals.
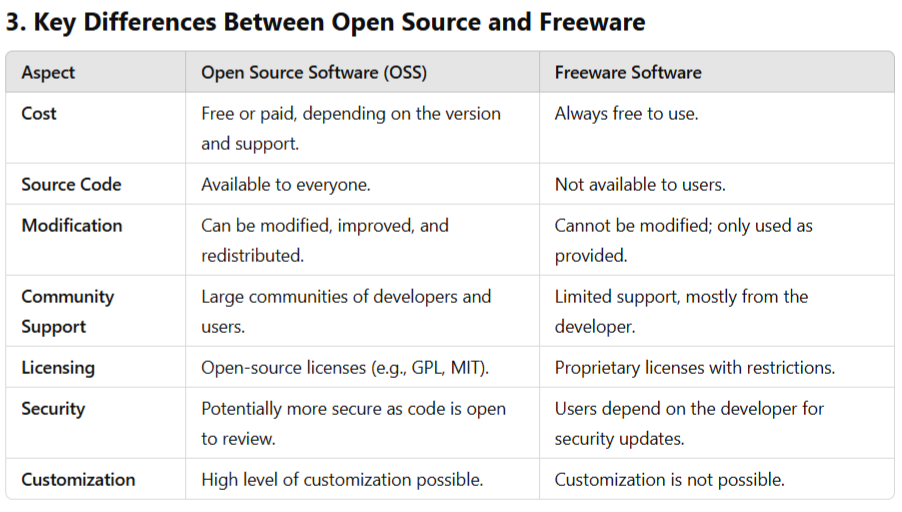
1. Open Source Software (OSS)
Definition:
Open Source Software is software that provides users with access to its source code. Users are free to use, modify, and distribute the software under the conditions set by the license (such as the GPL – General Public License). The open nature of OSS encourages collaboration and improvements by the user community.
Key Characteristics:
- Source Code Accessibility: The source code is publicly available for anyone to view, modify, or improve.
- Freedom to Modify: Users can customize the software to fit their specific needs or improve it.
- Collaboration: It fosters collaboration among developers, users, and communities to build better versions of the software.
- License Types: Open Source licenses (e.g., GPL, MIT) ensure users’ rights to use, share, and modify the software.
- Examples: Linux, Apache, Firefox, MySQL, DSpace.
Advantages for MLIS Students:
- Flexibility to tailor library management software to meet specific needs.
- Community support for problem-solving and software improvement.
- No licensing costs for the software itself, which can be beneficial for institutions with limited budgets.
Lecture: Difference Between Open Source Software and Freeware Software
Introduction:
In the field of Library and Information Science (LIS), understanding different types of software is crucial for managing digital libraries, databases, and information systems. Today, we will discuss two commonly misunderstood software categories: Open Source Software and Freeware Software. These terms are frequently used in the context of software distribution, but they have distinct differences in terms of licensing, usage, and access to the software’s source code.
Objectives:
- Define Open Source Software and Freeware.
- Compare the key differences between the two.
- Understand the implications of each for Library and Information Science (LIS) professionals.
2. Freeware Software
Definition:
Freeware is software that is available to users at no cost. However, unlike Open Source Software, freeware does not provide access to its source code. It is typically proprietary, and users are only allowed to use the software without modifying it.
Key Characteristics:
- No Cost: Free to download and use, but the developer retains all rights to the software.
- Closed Source: The source code is not available to the public, meaning users cannot modify or improve the software.
- Usage Restrictions: Though free, there may be restrictions on its use (e.g., non-commercial use, personal use only).
- Updates and Support: Users depend on the software developer for updates and support, which may be limited or absent.
- Examples: Adobe Acrobat Reader, Skype, Google Chrome (parts of it), WinRAR.
Advantages for MLIS Students:
- Easy access to necessary tools without needing to pay.
- Simple to use with no technical expertise required to modify code.
- Good for institutions or individuals who need functional software but lack IT support for managing open-source alternatives.
تعارف: لائبریری اور معلوماتی سائنس کے شعبے میں مختلف قسم کے سافٹ ویئرز کو سمجھنا بہت اہم ہے، کیونکہ یہ ڈیجیٹل لائبریریوں، ڈیٹا بیسز اور معلوماتی نظاموں کے انتظام کے لیے ضروری ہیں۔ آج ہم دو اہم سافٹ ویئر کیٹیگریز پر بات کریں گے: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر اور فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر۔ یہ دونوں شرائط اکثر ایک دوسرے کے ساتھ استعمال ہوتی ہیں لیکن ان کے لائسنس، استعمال اور سورس کوڈ تک رسائی میں واضح فرق ہوتا ہے۔
مقاصد:
- اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر اور فری وئیر کی تعریف کرنا۔
- دونوں کے درمیان اہم فرق کو سمجھنا۔
- لائبریری اور معلوماتی سائنس کے پیشہ ور افراد کے لیے ہر ایک کی اہمیت کا تجزیہ کرن
تعریف:
اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر وہ سافٹ ویئر ہوتا ہے جس کا سورس کوڈ صارفین کے لیے دستیاب ہوتا ہے۔ صارفین کو سافٹ ویئر کو استعمال، ترمیم اور تقسیم کرنے کی آزادی ہوتی ہے، بشرطیکہ وہ لائسنس (جیسے کہ GPL – جنرل پبلک لائسنس) کی شرائط کی پابندی کریں۔
اہم خصوصیات:
- سورس کوڈ تک رسائی: سورس کوڈ عوام کے لیے دستیاب ہوتا ہے، جسے کوئی بھی دیکھ، ترمیم یا بہتر کر سکتا ہے۔
- ترمیم کی آزادی: صارفین سافٹ ویئر کو اپنی ضروریات کے مطابق ڈھال سکتے ہیں۔
- تعاون: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کمیونٹی میں تعاون کو فروغ دیتا ہے، جہاں مختلف لوگ سافٹ ویئر کو بہتر بنا سکتے ہیں۔
- لائسنس کی اقسام: اوپن سورس لائسنس جیسے GPL یا MIT صارفین کو سافٹ ویئر استعمال کرنے اور شیئر کرنے کی اجازت دیتے ہیں۔
- مثالیں: لینکس، اپاچی، فائر فاکس، MySQL،
- DSpace۔
- لائبریری مینجمنٹ سافٹ ویئر کو اپنی مخصوص ضروریات کے مطابق ڈھالنے کی لچک۔
- مسئلہ حل کرنے اور سافٹ ویئر کی بہتری کے لیے کمیونٹی کی مدد۔
- محدود بجٹ والے اداروں کے لیے بغیر لائسنس فیس کے سافٹ ویئر دستیاب۔
2. فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر
تعریف:
فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر وہ ہوتا ہے جو بغیر کسی لاگت کے صارفین کو دستیاب ہوتا ہے۔ تاہم، اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کے برعکس، اس کا سورس کوڈ دستیاب نہیں ہوتا اور اسے عام طور پر ترمیم نہیں کیا جا سکتا۔
اہم خصوصیات:
- کوئی لاگت نہیں: مفت میں ڈاؤن لوڈ اور استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے، لیکن اس کا حق ملکیت ڈیولپر کے پاس ہوتا ہے۔
- بند سورس: سورس کوڈ عوام کو دستیاب نہیں ہوتا۔
- استعمال کی حدود: استعمال میں پابندیاں ہو سکتی ہیں جیسے ذاتی یا غیر تجارتی استعمال۔
- اپ ڈیٹس اور سپورٹ: اپ ڈیٹس اور سپورٹ ڈیولپر پر منحصر ہوتی ہے، جو کہ محدود ہو سکتی ہے۔
- مثالیں: ایڈوب ریڈر، اسکائپ، گوگل کروم، WinRAR۔
MLIS طلباء کے لیے فوائد:
- بغیر لاگت کے ضروری ٹولز تک آسان رسائی۔
- استعمال میں آسان اور ترمیم کی ضرورت کے بغیر کام کرنے کی صلاحیت۔
- ان افراد یا اداروں کے لیے موزوں جو تکنیکی مدد کے بغیر سادہ سافٹ ویئر استعمال کرنا چاہتے ہیں۔
2. فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر
تعریف:
فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر وہ ہوتا ہے جو بغیر کسی لاگت کے صارفین کو دستیاب ہوتا ہے۔ تاہم، اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کے برعکس، اس کا سورس کوڈ دستیاب نہیں ہوتا اور اسے عام طور پر ترمیم نہیں کیا جا سکتا۔
اہم خصوصیات:
- کوئی لاگت نہیں: مفت میں ڈاؤن لوڈ اور استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے، لیکن اس کا حق ملکیت ڈیولپر کے پاس ہوتا ہے۔
- بند سورس: سورس کوڈ عوام کو دستیاب نہیں ہوتا۔
- استعمال کی حدود: استعمال میں پابندیاں ہو سکتی ہیں جیسے ذاتی یا غیر تجارتی استعمال۔
- اپ ڈیٹس اور سپورٹ: اپ ڈیٹس اور سپورٹ ڈیولپر پر منحصر ہوتی ہے، جو کہ محدود ہو سکتی ہے۔
- مثالیں: ایڈوب ریڈر، اسکائپ، گوگل کروم،
- WinRAR۔
MLIS طلباء کے لیے فوائد:
- بغیر لاگت کے ضروری ٹولز تک آسان رسائی۔
- استعمال میں آسان اور ترمیم کی ضرورت کے بغیر کام کرنے کی صلاحیت۔
- ان افراد یا اداروں کے لیے موزوں جو تکنیکی مدد کے بغیر سادہ سافٹ ویئر استعمال کرنا چاہتے ہیں۔
4. Why Is This Important for MLIS Students?
- Software Selection: As future information professionals, selecting the right software is crucial for managing digital repositories, library automation, and data organization.
- Budget Constraints: Open-source software can save costs in resource-constrained libraries, while freeware offers free-to-use tools with less complexity.
- Customization vs. Ease of Use: Open-source software allows customization, but it may require technical skills. Freeware offers ease of use but lacks flexibility for modification.
- Ethical and Legal Issues: Understanding software licenses ensures compliance with legal obligations, especially in educational institutions.
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between Open Source Software and Freeware is essential for making informed decisions in managing digital systems in libraries. While both types of software are available at no cost, the openness of the source code and the ability to modify it are what primarily distinguish OSS from freeware.
As MLIS students, you must consider these factors when selecting tools that will support your roles as future librarians and information specialists.
Discussion Questions:
- Can you think of any freeware or open-source software you use in your daily studies?
- How would access to open source code benefit a digital library system?
- What are some challenges libraries might face when adopting open-source software?
Assignment:
- Research an open-source software used in libraries and present its advantages and disadvantages in your next class.
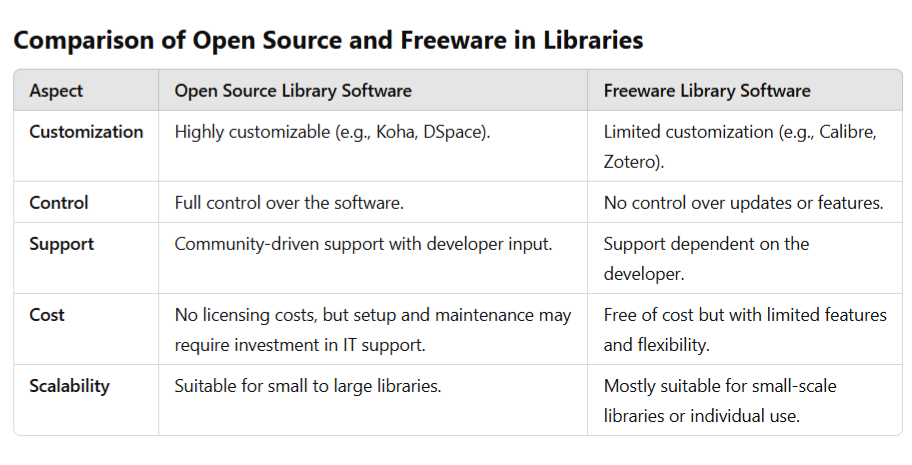
Open Source Library Software
Open Source Library Software allows libraries to access, modify, and redistribute software according to their specific needs. This flexibility is particularly valuable in resource-limited environments, such as academic or public libraries, where budget constraints are common.
Popular Open Source Library Software
Koha
- Description: Koha is one of the most widely used Integrated Library Systems (ILS). It offers full control to users for cataloging, circulation, and managing patron data.
- Features:
- Advanced cataloging tools (MARC records support).
- Customizable user interface.
- Strong community support with regular updates.
- Available in multiple languages.
- Advantages: Highly customizable and scalable for libraries of any size.
- Disadvantages: Requires technical skills for setup and maintenance.
Evergreen
- Description: Evergreen is another open-source ILS designed for consortia and public libraries. It supports multi-branch libraries with various automation tasks.
- Features:
- Manages multiple libraries with ease.
- Supports acquisitions, cataloging, circulation, and statistical reporting.
- Customizable and extendable.
- Advantages: Ideal for large library systems.
- Disadvantages: Like Koha, it requires in-house technical expertise or support services.
DSpace
- Description: DSpace is an open-source repository software that libraries use to build digital collections of research outputs, such as theses, articles, and datasets.
- Features:
- Preserves and manages digital content.
- Flexible metadata schemas (e.g., Dublin Core).
- Integrates with external services for enhanced discoverability.
- Advantages: Perfect for academic libraries and institutional repositories.
- Disadvantages: Can be complex to install without the appropriate IT skills.
VuFind
- Description: VuFind is an open-source discovery layer that libraries use to allow users to search multiple databases simultaneously, improving user experience.
- Features:
- Provides a simple, modern search interface.
- Faceted browsing for easier discovery.
- Flexible enough to integrate with various back-end systems like Koha or Evergreen.
- Advantages: User-friendly, enhances search experiences.
- Disadvantages: Requires technical knowledge for installation and configuration.
Freeware Library Software
Freeware software, while free of cost, does not offer the same flexibility as open-source software in terms of customization. Libraries can use these tools as they are, but they are dependent on the software developer for updates and support.
Popular Freeware Library Software
LibraryThing
- Description: LibraryThing is an online service used by libraries and individuals to catalog books and manage library collections.
- Features:
- Easily searchable catalog for books.
- Integrated social network for book lovers.
- Easy export and import of records.
- Advantages: No technical skills required, simple to use.
- Disadvantages: Limited scalability for larger libraries and no control over code.
Calibre
- Description: Calibre is a powerful eBook manager that is used by libraries to manage digital content, particularly eBooks.
- Features:
- Convert eBook formats.
- Organize eBooks in various categories.
- Sync with e-readers.
- Advantages: Great for small libraries with digital collections.
- Disadvantages: Not suitable for complex library management tasks (e.g., cataloging or circulation).
BiblioteQ
- Description: BiblioteQ is a freeware cataloging and library management solution. It’s simple and useful for small-scale libraries.
- Features:
- Cataloging support for books, DVDs, music CDs, and more.
- Simple graphical interface.
- Backup and restore capabilities.
- Advantages: Easy to use and set up.
- Disadvantages: Lacks some advanced features like integration with other systems.
Zotero
- Description: Zotero is a freeware reference management tool used by academic libraries and researchers for citation management.
- Features:
- Organizes research sources and bibliographies.
- Integrates with word processors for citation management.
- Collects metadata automatically from web pages and PDFs.
- Advantages: Free and widely used by researchers and libraries.
- Disadvantages: Not a full library management system, but useful for research support.
Why Open Source Is Preferred in Large Libraries
- Scalability: Open-source software like Koha and Evergreen can scale to manage large library systems, multiple branches, and extensive digital resources.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Open-source software does not have licensing fees, making it an affordable solution for libraries with limited budgets.
- Customization: Libraries can adapt open-source software to meet their specific needs. For example, a public library can tailor Koha to handle complex user memberships, book reservations, and fee management.
- Community Collaboration: Libraries using open-source systems can benefit from a global community of developers and librarians who contribute to the software’s improvement.
Challenges of Freeware in Large Libraries
- Limited Features: Freeware is usually designed for smaller libraries or individual use. For instance, while LibraryThing is a fantastic tool for personal or small library cataloging, it lacks the features necessary to handle circulation or detailed reporting.
- Dependence on Developer: Freeware users are often dependent on the developer for updates and improvements, which may not be as frequent or responsive as open-source community-driven software.
- No Customization: Freeware does not offer the flexibility to tailor the system to the library’s specific needs, which can be a drawback for larger, more complex institutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Software for Libraries
When deciding between open-source and freeware software, libraries must consider factors such as budget, technical capacity, scalability, and the specific needs of their institution. For smaller libraries with minimal technical requirements, freeware may provide a simple and effective solution. On the other hand, larger libraries or those with specific customization needs may find open-source software more suitable due to its flexibility, scalability, and active community support.
By understanding these distinctions, MLIS students can make informed decisions about which software solutions are best suited to their future work environments, ensuring they can effectively manage library resources and provide the best service to their patrons.
4. MLIS طلباء کے لیے اس کی اہمیت کیوں؟
- سافٹ ویئر کا انتخاب: ڈیجیٹل لائبریریوں، لائبریری آٹومیشن، اور ڈیٹا کے انتظام میں صحیح سافٹ ویئر کا انتخاب انتہائی ضروری ہے۔
- بجٹ کی پابندیاں: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر محدود وسائل والی لائبریریوں کے لیے لاگت بچانے کا ذریعہ ہو سکتا ہے، جبکہ فری وئیر آسان اور مفت حل فراہم کرتا ہے۔
- ترمیم بمقابلہ آسانی: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر میں ترمیم کی لچک ہوتی ہے، لیکن اس کے لیے تکنیکی مہارت درکار ہو سکتی ہے۔ فری وئیر استعمال میں آسان ہوتا ہے لیکن حسب ضرورت کی کمی ہوتی ہے۔
- اخلاقی اور قانونی مسائل: سافٹ ویئر کے لائسنس کو سمجھنا قانونی ذمہ داریوں کی تعمیل کو یقینی بناتا ہے، خاص طور پر تعلیمی اداروں میں۔
نتیجہ:
اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر اور فری وئیر کے درمیان فرق کو سمجھنا لائبریری کے نظاموں کے انتظام میں بہتر فیصلے کرنے میں مددگار ہوتا ہے۔ دونوں سافٹ ویئر مفت دستیاب ہو سکتے ہیں، لیکن ان کے سورس کوڈ کی دستیابی اور ترمیم کی صلاحیت بنیادی فرق ہیں۔
MLIS طلباء کو ان عوامل کو مدنظر رکھ کر وہ ٹولز منتخب کرنے چاہیے جو ان کی پیشہ ورانہ ضروریات کو پورا کرتے ہوں۔
بحث کے سوالات:
- کیا آپ روزمرہ کے مطالعے میں کوئی فری وئیر یا اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر استعمال کرتے ہیں؟
- ڈیجیٹل لائبریری سسٹم کے لیے سورس کوڈ تک رسائی کس طرح فائدہ مند ہو سکتی ہے؟
- لائبریریوں کو اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر اپنانے میں کن چیلنجز کا سامنا ہو سکتا ہے؟
اسائنمنٹ:
- لائبریریوں میں استعمال ہونے والے کسی اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر پر تحقیق کریں اور اس کے فوائد اور نقصانات کو اگلی کلاس میں پیش کریں۔
اوپن سورس لائبریری سافٹ ویئر
اوپن سورس لائبریری سافٹ ویئر لائبریریوں کو سافٹ ویئر تک مکمل رسائی، ترمیم اور دوبارہ تقسیم کی اجازت دیتا ہے۔ یہ لائبریریوں کے لیے ایک اہم فائدہ ہے، خاص طور پر ان لائبریریوں کے لیے جو بجٹ کے مسائل کا سامنا کرتی ہیں، جیسے کہ عوامی یا تعلیمی لائبریریاں۔
مشہور اوپن سورس لائبریری سافٹ ویئر
-
کوہا (Koha)
- تفصیل: کوہا ایک وسیع پیمانے پر استعمال ہونے والا انٹیگریٹڈ لائبریری سسٹم (ILS) ہے۔ یہ صارفین کو کیٹلاگنگ، سرکولیشن، اور پیٹرن ڈیٹا مینجمنٹ کی مکمل کنٹرول فراہم کرتا ہے۔
- خصوصیات:
- جدید کیٹلاگنگ ٹولز (MARC ریکارڈز کی حمایت)۔
- یوزر انٹرفیس کو حسب ضرورت بنایا جا سکتا ہے۔
- بڑی کمیونٹی سپورٹ اور باقاعدہ اپ ڈیٹس۔
- کئی زبانوں میں دستیاب۔
- فائدے: بہت زیادہ حسب ضرورت اور ہر سائز کی لائبریریوں کے لیے موزوں۔
- نقصانات: سیٹ اپ اور مینٹیننس کے لیے تکنیکی مہارت کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے
-
- ایورگرین (Evergreen)
- تفصیل: ایورگرین ایک اوپن سورس ILS ہے جو خاص طور پر کونسورٹیا اور عوامی لائبریریوں کے لیے بنایا گیا ہے۔ یہ مختلف خودکار کاموں کے ساتھ متعدد شاخوں والی لائبریریوں کو سپورٹ کرتا ہے۔
- خصوصیات:
- آسانی سے متعدد لائبریریوں کا انتظام کرتا ہے۔
- حصولات، کیٹلاگنگ، سرکولیشن، اور رپورٹنگ کو سپورٹ کرتا ہے۔
- حسب ضرورت اور توسیع پذیر۔
- فائدے: بڑی لائبریری سسٹمز کے لیے موزوں۔
- نقصانات: کوہا کی طرح، اس میں تکنیکی مہارت یا سپورٹ سروسز کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔
ڈی اسپیس (DSpace)
- تفصیل: DSpace ایک اوپن سورس ریپوزٹری سافٹ ویئر ہے جو لائبریریاں تحقیقاتی مواد جیسے مقالے، مضامین اور ڈیٹا سیٹس کو ڈیجیٹل مجموعے بنانے کے لیے استعمال کرتی ہیں۔
- خصوصیات:
- ڈیجیٹل مواد کو محفوظ کرتا ہے اور اس کا انتظام کرتا ہے۔
- مختلف میٹا ڈیٹا اسکیموں کی لچک (جیسے Dublin Core)۔
- مواد کی دریافت کو بہتر بنانے کے لیے بیرونی سروسز کے ساتھ انضمام۔
- فائدے: تعلیمی لائبریریوں اور ادارہ جاتی ریپوزٹریز کے لیے بہترین۔
- نقصانات: بغیر مناسب آئی ٹی مہارت کے انسٹال کرنا مشکل ہو سکتا ہے۔
-
- تفصیل: VuFind ایک اوپن سورس ڈسکوری لیئر ہے جو لائبریریاں متعدد ڈیٹا بیسز کو ایک ساتھ تلاش کرنے کے لیے استعمال کرتی ہیں، جس سے صارفین کا تجربہ بہتر ہوتا ہے۔
- خصوصیات:
- ایک سادہ، جدید تلاش کا انٹرفیس فراہم کرتا ہے۔
- فیسٹیڈ براؤزنگ کے ذریعے آسانی سے مواد کی دریافت۔
- مختلف بیک اینڈ سسٹمز (جیسے کوہا یا ایورگرین) کے ساتھ انضمام کی صلاحیت۔
- فائدے: صارف دوست، تلاش کے تجربات کو بہتر بناتا ہے۔
- نقصانات: انسٹالیشن اور کنفیگریشن کے لیے تکنیکی معلومات کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔
-
فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر مفت ہوتا ہے، لیکن یہ اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کی طرح حسب ضرورت یا کنٹرول فراہم نہیں کرتا۔ لائبریریاں ان ٹولز کو ویسے ہی استعمال کرتی ہیں جیسا کہ وہ فراہم کیے گئے ہیں،
مشہور فری وئیر لائبریری سافٹ
-
LibraryThing
- تفصیل: LibraryThing ایک آن لائن سروس ہے جو لائبریریاں اور افراد کتابوں کو کیٹلاگ کرنے اور لائبریری مجموعوں کا انتظام کرنے کے لیے استعمال کرتے ہیں۔
- خصوصیات:
- کتابوں کے لیے آسانی سے تلاش کیا جانے والا کیٹلاگ۔
- کتابوں کے شوقین افراد کے لیے ایک سوشل نیٹ ورک کا حصہ۔
- ریکارڈز کو درآمد اور برآمد کرنے کی آسانی۔
- فائدے: آسان، تکنیکی مہارت کی ضرورت نہیں۔
- نقصانات: بڑی لائبریریوں کے لیے محدود اسکیلنگ اور کوڈ کا کوئی کنٹرول نہیں۔
-
Calibre
- تفصیل: Calibre ایک طاقتور ای بُک مینیجر ہے جو لائبریریاں ڈیجیٹل مواد، خاص طور پر ای بُکس کو منظم کرنے کے لیے استعمال کرتی ہیں۔
- خصوصیات:
- ای بُک فارمیٹس کو کنورٹ کرتا ہے۔
- ای بُکس کو مختلف کیٹیگریز میں منظم کرتا ہے۔
- ای ریڈرز کے ساتھ ہم آہنگی۔
- فائدے: چھوٹی لائبریریوں کے لیے بہترین، جن کے پاس ڈیجیٹل مجموعے ہوں۔
- نقصانات: پیچیدہ لائبریری مینجمنٹ ٹاسک کے لیے موزوں نہیں۔
-
BiblioteQ
- تفصیل: BiblioteQ ایک فری وئیر کیٹلاگنگ اور لائبریری مینجمنٹ سلوشن ہے، جو چھوٹے پیمانے پر لائبریریوں کے لیے استعمال کیا جاتا ہے۔
- خصوصیات:
- کتابوں، ڈی وی ڈیز، میوزک CDs وغیرہ کی کیٹلاگنگ سپورٹ۔
- سادہ گرافیکل انٹرفیس۔
- بیک اپ اور ریسٹور کی خصوصیات۔
- فائدے: آسان، سیٹ اپ میں آسان۔
- نقصانات: محدود جدید خصوصیات، جیسے کہ دوسرے سسٹمز کے ساتھ
- انضمام۔
-
Zotero
- تفصیل: Zotero ایک فری وئیر ریفرنس مینجمنٹ ٹول ہے جو تعلیمی لائبریریوں اور محققین کے ذریعہ حوالہ جات کے انتظام کے لیے استعمال ہوتا ہے۔
- خصوصیات:
- تحقیقاتی ذرائع اور ببلائیوگرافی کو منظم کرتا ہے۔
- حوالہ جات کے انتظام کے لیے ورڈ پروسیسرز کے ساتھ انضمام۔
- ویب صفحات اور PDFs سے خودکار طور پر میٹا ڈیٹا اکٹھا کرتا ہے۔
- فائدے: مفت اور محققین اور لائبریریوں میں وسیع پیمانے پر استعمال ہوتا ہے۔
- نقصانات: مکمل لائبریری مینجمنٹ سسٹم نہیں، لیکن تحقیقاتی سپورٹ کے لیے مفید۔اور ان کا انحصار ڈیولپر پر ہوتا ہے
-
بڑی لائبریریوں میں اوپن سورس کیوں بہتر ہے؟
- اسکیل ایبلٹی: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر جیسے کوہا اور ایورگرین بڑی لائبریری سسٹمز، متعدد شاخوں، اور وسیع ڈیجیٹل وسائل کو منظم کرنے کی صلاحیت رکھتے ہیں۔
- بجٹ کے لیے موزوں: اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر میں لائسنسنگ فیس نہیں ہوتی، جس سے بجٹ میں محدود لائبریریوں کے لیے یہ ایک سستا حل بنتا ہے۔
- حسب ضرورت: لائبریریاں اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کو اپنی مخصوص ضروریات کے مطابق بنا سکتی ہیں۔ مثال کے طور پر، ایک عوامی لائبریری کوہا کو ممبرشپ، بکنگ، اور فیس مینجمنٹ کے لیے مخصوص خصوصیات کے ساتھ حسب ضرورت بنا سکتی ہے۔
- کمیونٹی تعاون: اوپن سورس سسٹم استعمال کرنے والی لائبریریاں دنیا بھر کی کمیونٹی سے فائدہ اٹھا سکتی ہیں جو سافٹ ویئر کی بہتری میں حصہ لیتی ہیں۔
بڑی لائبریریوں میں فری وئیر کی مشکلات
- محدود خصوصیات: فری وئیر اکثر چھوٹی لائبریریوں یا انفرادی استعمال کے لیے بنایا جاتا ہے۔ مثال کے طور پر، جبکہ LibraryThing کتابوں کی کیٹلاگنگ کے لیے ایک بہترین ٹول ہے، یہ سرکولیشن یا تفصیلی رپورٹنگ جیسے اہم فیچرز فراہم نہیں کرتا۔
- ڈیولپر پر انحصار: فری وئیر استعمال کرنے والے صارفین اپ ڈیٹس اور بہتری کے لیے ڈیولپر پر انحصار کرتے ہیں، جو اوپن سورس کے مقابلے میں کم تسلسل سے ہوتا ہے۔
- حسب ضرورت کی کمی: فری وئیر لائبریری کی مخصوص ضروریات کے مطابق سسٹم کو ترتیب دینے کی لچک فراہم نہیں کرتا، جو بڑی اور پیچیدہ لائبریریوں کے لیے نقصان دہ ہو سکتا ہے۔
نتیجہ: لائبریریوں کے لیے صحیح سافٹ ویئر کا انتخاب
اوپن سورس اور فری وئیر سافٹ ویئر میں سے انتخاب کرتے وقت، لائبریریوں کو بجٹ، تکنیکی صلاحیت، اسکیل ایبلٹی اور ان کی مخصوص ضروریات کو مدنظر رکھنا چاہیے۔ چھوٹی لائبریریوں کے لیے، جو تکنیکی ضروریات کم ہیں، فری وئیر ایک سادہ اور مؤثر حل فراہم کر سکتا ہے۔ دوسری طرف، بڑی لائبریریاں یا وہ لائبریریاں جن کو حسب ضرورت کی ضرورت ہو، اوپن سورس سافٹ ویئر کو زیادہ موزوں پاتی ہیں۔
مزید مطالعہ کے لیے:
ایم ایل آئی ایس طلباء مزید سمجھنے کے لیے کوہا یوزر گروپ یا ڈی اسپیس کمیونٹی جیسے آن لائن کمیونٹیز کا دورہ کر سکتے ہیں کہ یہ اوپن سورس پلیٹ فارم کیسے ترقی کرتے ہیں اور کس طرح کمیونٹی اور ڈیولپر ان کی مدد کرتے ہیں۔
