Ch. Bakht Yar Zafar
Koha Library software with full feature and Historical backgrounds
Abstarct
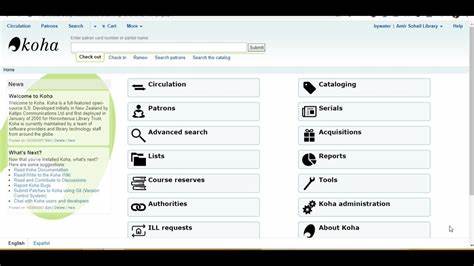
Koha is an open-source Integrated Library System (ILS) that is used by libraries of all types and sizes to manage their collections and services. It was first developed in 1999 by a New Zealand-based web development company, Katipo Communications, and has since grown to become one of the most widely adopted open-source ILSs.
Koha offers a wide range of features that allow libraries to efficiently manage their catalog, circulation, acquisitions, and patron management. It also includes modules for serials management, reporting and analytics, self-checkout and RFID integration, and web-based access to the catalog.
One of the key strengths of Koha is its user-friendly and customizable interface, which makes it easy for librarians to navigate and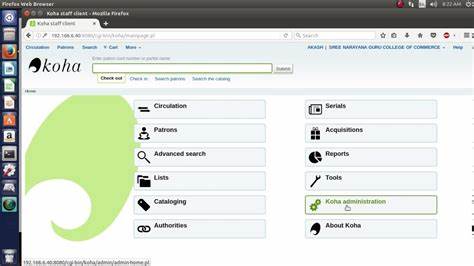 manage the system. Additionally, Koha is actively developed and supported by a global network of volunteer developers and contributors, which ensures that the software is continuously updated and improved.
manage the system. Additionally, Koha is actively developed and supported by a global network of volunteer developers and contributors, which ensures that the software is continuously updated and improved.
In summary, Koha is a powerful, versatile and open-source library management system that can be tailored to the needs of any library. With its comprehensive feature set, Koha can help libraries improve the efficiency of their operations and provide better services to their patrons.
Introduction
Koha is an open-source Integrated Library System (ILS) that was first developed in 1999 by Katipo Communications, a New Zealand-based web development company. The name “Koha” is a Maori word that means “gift” or “donation,” reflecting the open-source nature of the software.
Koha was originally developed for Horowhenua Library Trust, a library in New Zealand, as a way to replace their proprietary ILS. The software was later released as open-source under the GNU General Public License in 2000, making it the first open-source ILS to be widely adopted by libraries around the world.
Since its initial release, Koha has been adopted by libraries of all types and sizes, including public, academic, and special libraries. It has a strong user community and is actively developed and supported by a global network of volunteer developers and contributors.
Koha has a number of features that set it apart from other ILSs, including a user-friendly and customizable interface, a robust set of circulation and cataloging tools, and support for a wide range of databases and operating systems. It also includes modules for acquisitions, serials management, and patron management.
In recent years, Koha has continued to evolve and improve, with new features and enhancements being added regularly. It’s now one of the most widely used open-source ILS and supported by a large community of developers, librarians and other stakeholders.
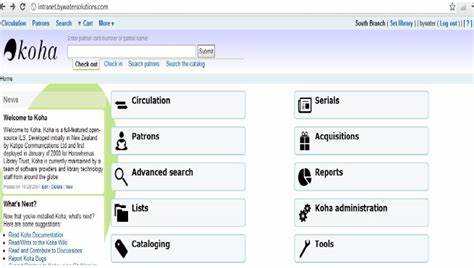
Feature
Koha is an open-source Integrated Library System (ILS) that offers a wide range of features to help libraries manage their collections and services. Some of the key features of Koha include:
- Cataloging: Koha includes powerful cataloging tools that allow librarians to easily create, edit, and manage bibliographic records, including MARC and RDA support.
- Circulation: Koha offers a comprehensive circulation module that allows libraries to manage the lending of materials, including the ability to create holds, check in and check out items, and generate overdue notices.
- Acquisitions: Koha includes tools for managing the purchase and receipt of library materials, including budget tracking and invoice management.
- Patron Management: Koha offers a patron management module that allows libraries to create, update, and manage patron records, including contact information, check-out history, and fines.
-
Serials Management: Koha includes a serials management module that allows libraries to track and manage serial publications, including subscriptions and the receipt of individual issues.

- Reporting and Analytics: Koha offers a wide range of reports and analytics, including circulation reports, cataloging reports, and acquisitions reports, which help libraries to track usage, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Self-Checkout and RFID Integration: Koha allows libraries to set up self-checkout stations and integrate RFID technology to streamline the check-out process.
- Web-based Access: Koha provides web-based access to the catalog, patron accounts, and other library services, making it easy for patrons to access information and manage their accounts from anywhere.
- Mobile Access: Koha has mobile-friendly interfaces for patrons to access their account and check-out materials.
- Automatic Authority Control: Koha has inbuilt functionality to automatically match authority records and improve the quality of cataloging.
- Digital Asset Management: Koha includes digital asset management features that allow libraries to store, manage, and provide access to digital resources.
These features make Koha a powerful and versatile library management system that can be tailored to meet the needs of any library.
Koha is generally considered to be a reliable and robust library management system that offers a wide range of features to help libraries manage their collections and services. However, as with any software, there are some criticisms and limitations that have been noted by users.
One of the criticisms of Koha is that its user interface can be difficult to navigate for those who are not familiar with it. While the interface is considered to be relatively user-friendly, it can take some time for new users to learn how to use all of the features and functions.
Another criticism of Koha is that it can be difficult to customize the software to meet the specific needs of a library. While Koha is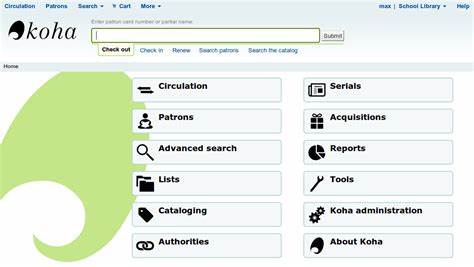 designed to be flexible and customizable, it can be challenging for libraries to make significant changes to the software without the help of a developer.
designed to be flexible and customizable, it can be challenging for libraries to make significant changes to the software without the help of a developer.
Another limitation of Koha is that it is not as widely used as other proprietary library management systems, which means that libraries may have a harder time finding support and resources compared to those using proprietary systems.
It’s also worth mentioning that Koha being open-source, the support and customization will depend on the library’s own IT department or the company that is hired to support and customize it.
Overall, Koha is widely used and well-regarded open-source library management system that offers a comprehensive set of features to help libraries manage their collections and services. However, like any software, there are some criticisms and limitations that should be considered before implementing it.
